The journey with dementia brings changes in an individual’s life. But it also opens up opportunities to connect, understand, and care in meaningful ways. Thus, when you know your loved one’s stage of dementia, you can give the right kind of support and make each day more comfortable and positive.
How can you find out which stage your loved one is in?
The Functional Assessment Staging Test is an essential test for the assessment of functional abilities and temporal deterioration in dementia patients. This tool divides Dementia into various stages. Finding your loved one’s overall score on the FAST scale Dementia tool will help the caregivers provide the best care and support.
Let’s dive deep into this blog and explore more about FAST Scale in depth!
What is the FAST Scale Dementia Tool?
FAST Scale primarily addresses the issue of assessing the development of Dementia. It categorizes Dementia into seven stages, which range from very mild to severe.
The FAST Scale was developed by Dr. Barry Reisberg in the 1980s to help measure how Alzheimer’s and other types of dementia affect a person’s daily life. Instead of just testing memory, it looks at how someone manages everyday tasks like dressing, bathing, talking, and remembering routines. This helps families better understand how their loved one’s condition is changing over time.
Understanding Dementia and Its Types
Dementia is a general term for a group of conditions that affect the brain and change a person’s mood, behavior, and ability to care for themselves. Alzheimer’s disease is the most common type, but there are several others, too. Here’s how the decline may look in other conditions:
| Type of Dementia | How It Progresses | Common Symptoms or Signs |
| Vascular Dementia | Often progresses in steps after small strokes | Trouble with planning, reasoning, and slowed thinking. May appear suddenly after a stroke. |
| Lewy Body Dementia | Includes fluctuating cognition, vivid dreams, or movement stiffness | Visual hallucinations, sleep disturbances, and Parkinson-like movement issues. |
| Frontotemporal Dementia | Affects personality, judgment, and speech earlier than memory | Behavior changes, poor decision-making, loss of empathy, or speech difficulties. |
| Mixed Dementia | Combines features of two or more types, making symptoms more varied | Unpredictable changes in memory, mood, and physical ability, depending on the mix. |
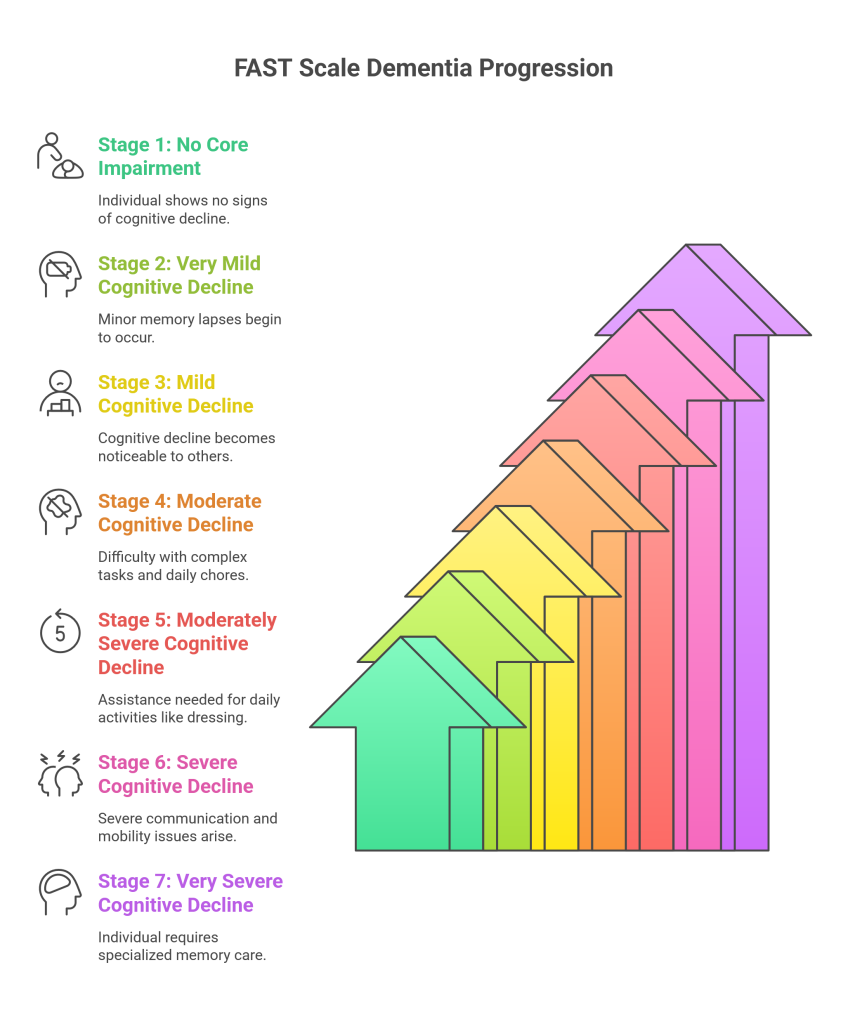
Seven Core Stages of Dementia
Each stage describes the individual’s abilities and needs. This helps caregivers and healthcare providers understand at which stage the person with Dementia is in their journey. Moreover, every stage, from initial to last-stage dementia, requires different care for patients.
Stage 1: No Core Impairment
Everything seems normal in the initial stage, as there are no signs of Dementia symptoms. The person functions just like a normal person. However, they may sometimes experience occasional memory lapses.
Stage 2: Very Mild Cognitive Decline
In the second stage, small changes may begin to appear in individuals with Dementia. The person starts forgetting things more often, like keys and other things. These issues may be minor and don’t affect daily life significantly.
Stage 3: Mild Cognitive Decline
In this stage, measured on the FAST scale dementia tool, the decline becomes more noticeable in individuals who have Dementia. The person struggles with tasks that used to be easy in the earlier days. Moreover, they may have gaps in memory or be unable to find the right words following the conversations. In this stage, others start witnessing a cognitive decline in individuals with Dementia.
Stage 4: Moderate Cognitive Decline
In stage 4, an individual might have difficulty doing complex tasks, such as managing finances or planning events. Individuals may require help to keep track of their medications and do daily chores.
Stage 5: Moderately Severe Cognitive Decline
The person requires help with doing everyday activities like dressing or bathing. They may need assistance and guidance to perform everyday activities.
Stage 6: Severe Cognitive Decline
In stage 6, severe impairment is seen in individuals with Dementia. They cannot communicate and have trouble understanding or responding to simple questions, like remembering their names. However, they may also face mobility issues, making walking or moving more challenging. Many individuals start showing “sub-stages” of decline.
|
Sub-Stage |
Description |
|
6a |
Trouble dressing properly without help |
|
6b |
Difficulty bathing or managing hygiene |
|
6c |
Forgetting toileting routines |
|
6d |
Occasional urinary incontinence |
|
6e |
Fecal incontinence and full dependence on caregivers |
Stage 7: Very Severe Cognitive Decline
In the final stage, an individual has advanced Dementia symptoms. They struggle with movement and lose the ability to sit up or hold their head up. So, they require specialized memory care and assistance to cover every aspect of daily life. You can check out the blog to explore different memory care options for your loved ones, such as in-home or assisted living. Stage 7 also includes smaller sub-stages that show how physical and verbal abilities decline over time:
|
Sub-Stage |
Description |
|
7a |
Limited speech, often just a few words per day |
|
7b |
Single-word communication |
|
7c |
Inability to walk without support |
|
7d |
Cannot sit up without assistance |
|
7e |
Cannot smile |
|
7f |
Cannot hold head upright |
Why Utilize the FAST Scale Dementia Tool?
Healthcare professionals use the FAST Scale to get insights into the progression of Dementia stages. Moreover, it is used for:
- Planning Right Care: Each dementia stage requires a specialized caregiving plan to meet the patient’s requirements. The FAST Scale dementia tool enables professionals to analyze your loved one’s dementia stage to offer the best caregiver plan.
- Preparing for Future Needs: The FAST scale sets a roadmap to help families prepare for future needs as the condition progresses. The families can understand what they must go through with each stage progression.
- Providing Right Resources: The FAST scale provides insight into the stage of Dementia your loved one is facing. Once aware of the specific stage of Dementia that your loved one faces, you can make informed decisions regarding the provision of appropriate care services.
- Emotional Support: Full information concerning the stage of Dementia facing a loved one can help families and caregivers understand how many challenges may lie ahead, give them direction, and help them seek emotional support.
The FAST Scale can also help doctors decide if someone might be ready for hospice care. A score of “7A” or higher usually means the person is in the final stage of dementia, which may make them eligible for hospice under Medicare rules. Hospice care focuses on comfort, dignity, and emotional peace instead of aggressive treatments, helping both the person and their family have the best quality of life possible.
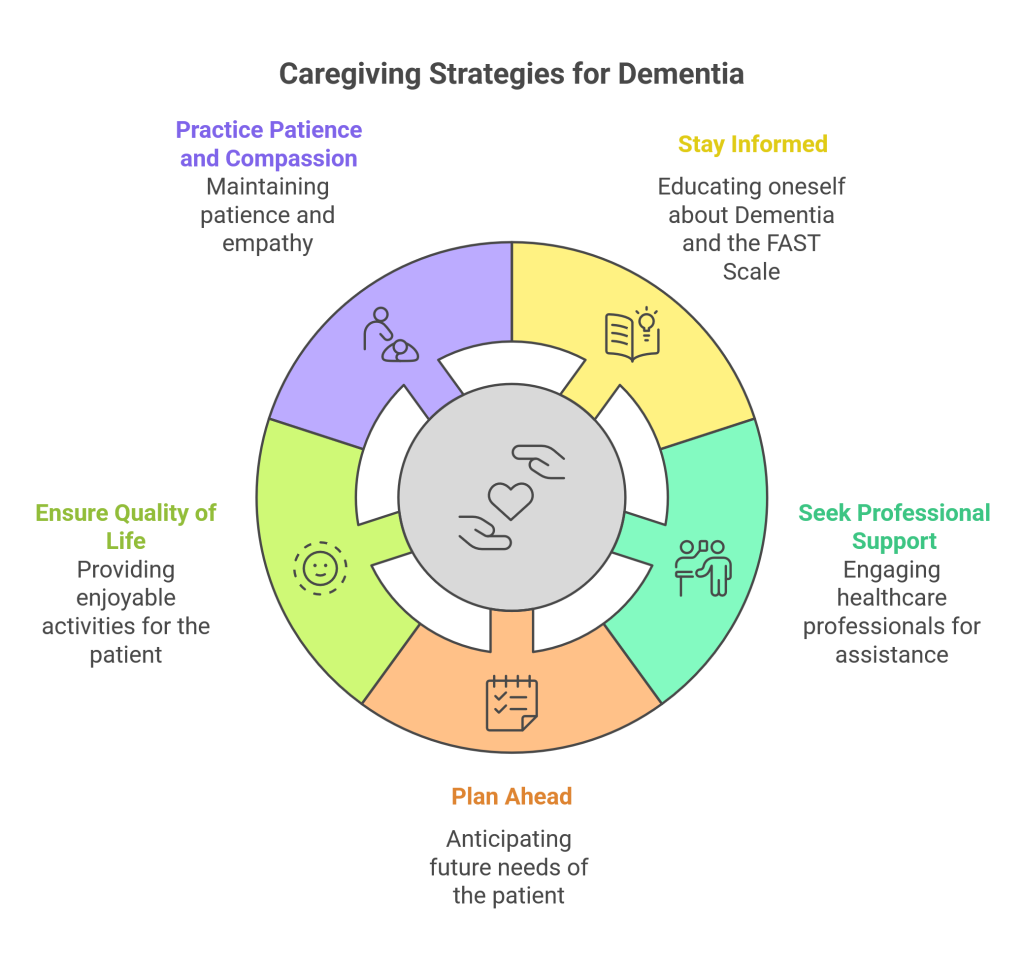
Essential Tips for Caregivers: Navigating Dementia with the FAST Scale
Caring for a loved one with Dementia can make a significant difference in managing their journey using the FAST scale Dementia tool. The Functional Assessment Staging Test breaks Dementia into different stages and helps caregivers navigate the complexities of dementia care. Here are some of the tips caregivers should follow:
- Stay Informed: You should educate yourself about Dementia and the FAST Scale to understand the disease and how to provide better care to your loved ones.
- Seek Support From Health Professionals: Caregiving is demanding and requires resilience and patience to address various sufferer’s needs. You should reach out to healthcare professionals for extensive support, like medical care and financial planning.
- Plan Ahead: You should recognize the patient’s future needs and plan everything to provide your loved ones with the best care and daily activities.
- Better Quality of Life: As the disease progresses, you need to ensure that you offer your loved ones the best quality of life. Therefore, provide activities that make you and your loved ones feel good and happy.
- Practice patience and compassion: Challenges brought by Dementia might be frustrating and may affect both the caregivers and the one experiencing its symptoms. You should be patient enough to support your loved ones in the progression of the disease.
To make caregiving easier, here’s a quick reference:
|
FAST Stage Range |
Care Focus |
Tips for Caregivers |
|
1–3 |
Early awareness | Encourage independence, mental stimulation, and consistent routines. |
|
4–5 |
Moderate decline | Simplify daily activities, use reminders, and maintain structure. |
|
6–7 |
Advanced care | Focus on comfort, gentle communication, and emotional connection through music or touch. |
Wrapping Up
Assessing the progression of the disease has become easy now with the FAST Scale Dementia tool. It provides a structured way to assess dementia stages. It allows caregivers to adopt an approach that provides the best care to individuals with Dementia. Therefore, caregivers will navigate the Dementia journey with greater awareness.
If you have any queries, you can get in touch with us for more details regarding the Dementia care plans for your loved ones! We know that every dementia journey is different. Our caring team offers personalized memory care, family support, and emotional guidance to ensure comfort and dignity at every stage.